Gary Boyle is an astronomy educator, guest speaker and monthly columnist for the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada (RASC), as well as past president of the Ottawa Centre of the RASC.
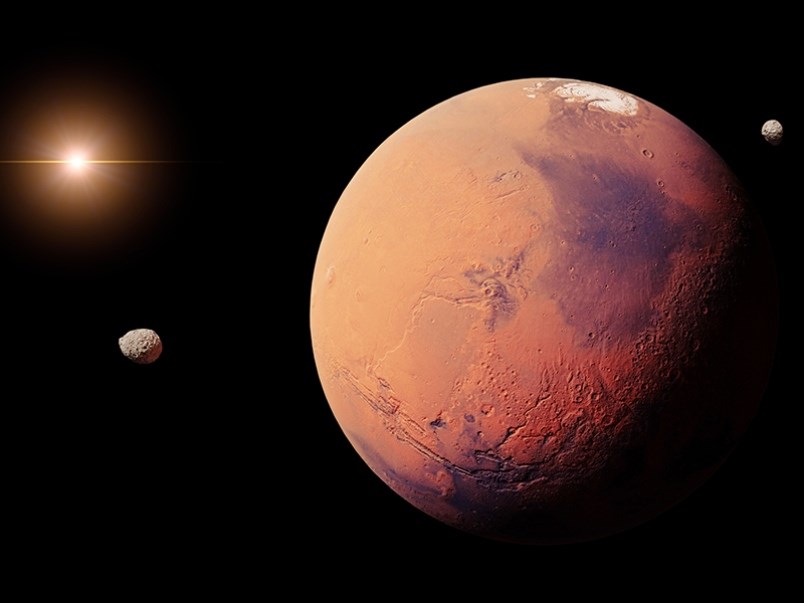
Some three billion years ago, Mars was believed to have been a water world just like Earth.
It possessed great oceans and was most likely on its way to forming life. Water is made up of hydrogen, the most common element in the universe and oxygen, the third most common element. Water is extremely important to the development and sustaining of life as we know it.
Because Mars is half the size of the earth, the planet lost its heat faster as its internal core stopped rotating.
Similar to earth’s core which produces a magnetic field around our planet, Mars' core ceased producing its protective magnetic field thus allowing the solar winds to eat away at its atmosphere and the red planet lost its water.
Ever since the early telescopic observations made by the Italian astronomer Giovanni Schiaparelli in 1877 when Mars was in opposition, residing 56 million km away, he is said to have seen "canali" or channels on Mars. Seeing these features gave the impression of a possible civilization.
Since then, the red planet has been the focus of searching for ancient life and is also the base of science fiction writers and movie makers.
By the 2030s or 2040s, humans are expected to land on this fascinating world, looking for the possibility of life that might have once existed, even at the microbial level.
After all, life is life. But Mars is now in the news for other reasons, it is now a very visible object in the night sky.
Appearing as a bright-orange object rising in the northeast sky about 45 minutes after the sun sets in the west, Mars is nicely placed amongst the bright winter constellations of Orion the Hunter, Taurus the Bull, etc.
If you are still not sure where to look, any smartphone astronomy app will guide you.
So why is it so bright?
Earth orbits the Sun in 365 days whereas Mars does so in 687 days. Just like the inner lap on a race track, Earth catches up and overtakes slower Mars every 26 months. This upcoming opposition will occur on Dec. 8 at a separation of only 82 million km.
Over the weeks after opposition, our distance increases and Mars will slowly fade. Every seventh opposition is super close such as back in 2003 and 2020. The next opposition occurs on Jan. 15, 2025.
Be sure to look at Mars the night before (Dec. 7) as the Full Cold Moon will cover Mars for a little less than one hour.
All of Canada, as well as much of the U.S., except for Alaska and the southeastern states, will see this amazing sight.
Throughout its 29.5-day orbit around the earth, the moon moves its width every hour. Throughout the month, it covers stars as seen through a telescope and in rare events, bright planets.
This should be a fantastic photo opportunity as the disappearance and later reappearance should be quite evident.